INTELLIGENT HOME SYSTEM
Focuses on the quality of life and security while providing solutions that increase comfort and entertainment.

Focuses on the quality of life and security while providing solutions that increase comfort and entertainment.
Our intelligent home will be implemented as a wireless home network, with every device in the house being a node (or connection point) of this network. Even the home residents, by carrying wearable sensors, will belong to the home network. The nodes will be continually collecting data from the environment and ISHA will react based on the information obtained.
Users will be able to interact with the intelligent home by using a computer, smartphone or tablet, as well as by giving the house direct voice or gesture commands.
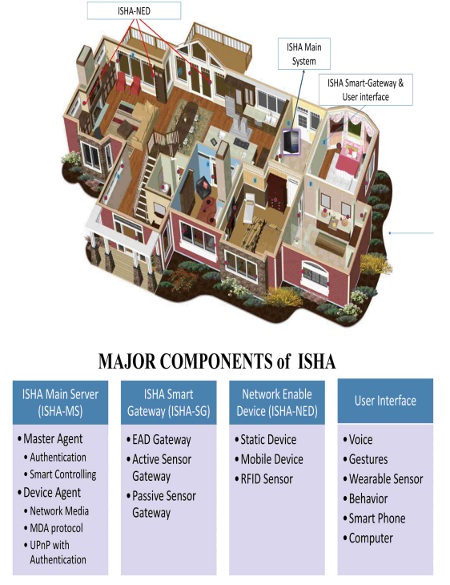
You are sitting in your living room watching television. ISHA detects that your body temperature is raising and your heartbeat is getting faster. The house detects that you are in the living room and turns on the air conditioning only in that room.
– Statistics Game (Untitled)

The four entrepreneurs have combined training in hyper-scale distributed financial systems, decentralized Bitcoin applications, artificial intelligence algorithms, and developing machine learning. The group was drawn from the two universities — Stone Hill College and Florida International University (FIU) — and their company, Master Branch is a startup that competed against 20 other companies for the final prize of US$100,000. For the competition, they named their team Decentral Bank to reflect their ideas.
The team was the only university group in the competition, as well as the only team to present a Bitcoin solution that will allow banks to accept Bitcoin without actually managing cryptocurrencies. They accomplished the task by implementing multisig technology. You can view the white paper here……
On Saturday, May 24, Dr. Jong-Hoon Kim and his staff were the main event of our final Burn Your Brain event of the semester. They presented the Discovery Lab’s QuadCopter project, showing the 25 attendees the technical ins and outs of building robotic flying devices. The students also learned how to write code to interpret realtime data from the same types of motion sensors used in robotic flying devices. Kim was assisted by Deon Wilkins, Fernando Campo, and Jaime Acevedo from the Discovery Lab. This was the 5th and final Burn Your Brain event of the semester, which has now reached approximately 120 computer students from Dade and Broward counties.
Thank you for all student members, volunteers, and staff for hosting an open house event as part of the National Robotics Week for an enthusiastic 230 registered attendees.
Efficient Concurrent Operations of Telepresence Avatars
Jong-Hoon Kim, Nagarajan Prabakar, Cynthia Tope
Abstract
Telepresence robot extends operation in remote locations as avatars. The remote physical presence application will enable individuals with mobility limitations such as disabled veteran or police officer to perform regular duties through telepresence robots known as avatars or TeleBots. Certain scenarios require many officers to operate on several TeleBots (1:1, 1:many, many:1, or many:many) in the same service area. Thus, we need an intelligent, fault tolerant management system to support these scenarios.
This system requires dynamic resource allocation such as communication bandwidth, battery power, spatial proximity, etc. In addition, conflicts among the concurrent telepresence operations need to be resolved efficiently. We propose a novel architecture that provides a fault tolerant multi telepresence robot Management System. This system will allow us to coordinate the assignment, scheduling, monitoring, and administrating multi telepresence robots and multi operators efficiently. Further, we present strategies to resolve conflicts among concurrent operations.
Full paper : ISR-13_Concurrent_Avatars.pdf
Standardized Linearization and Vectorization Algorithm for Arm Motion Control of A Humanoid Telepresence Robot
Michael Waddell, Joel Villasuso, Daniela ChavezGuevera, and Jong-Hoon Kim
Abstract
Recently, the new motion sensor: the Kinect is being used for natural motion retrieval with no additional equipment on the operator, less computational demand, and it is cost effective. But many restrictions apply because the results retrieved from the Kinect include noisy data which disturbs precise and smooth robot motion control. We propose a simple linearization algorithm to improve the accuracy of the data retrieved from the Kinect and designed a vectorization algorithm for converting positions of an operator’s skeleton in three dimensions to robot motions. In this paper, we provide the algorithm and its implementation. Furthermore, we demonstrate the performance of the algorithm using the prototype robot.
Full paper : ISR-13-ArmMotion.pdf